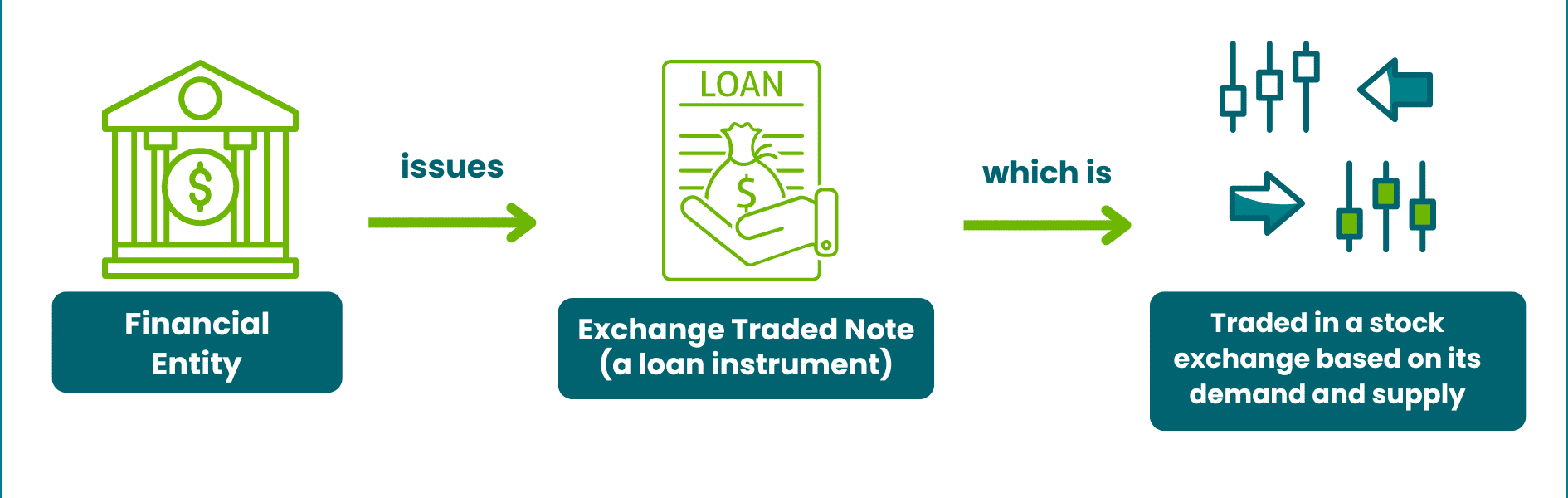
Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs) represent a unique class of investment products, offering exposure to various market sectors and asset classes․ Unlike Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), ETNs are debt instruments backed by an issuing financial institution․ This distinction introduces a different set of risks and rewards for investors to consider․ Understanding the nuances of ETNs is crucial for making informed investment decisions and diversifying portfolios effectively․
ETNs are senior, unsecured debt securities issued by a financial institution․ They promise to pay the return of a market index or other benchmark, less investor fees․ This section delves into the key characteristics of ETNs․
Key Characteristics of ETNs
Here’s a breakdown of some of the core features that define ETNs:
- Debt Instrument: ETNs are debt obligations of the issuing bank․
- Tracking an Index: They aim to replicate the performance of a specific index, commodity, or investment strategy․
- No Underlying Assets: Unlike ETFs, ETNs don’t hold the underlying assets they track․
- Credit Risk: Investors are exposed to the creditworthiness of the issuing bank․
- Expense Ratio: ETNs charge an expense ratio, similar to ETFs, to cover management and operational costs․
ETNs vs․ ETFs: A Comparative Analysis
While both ETNs and ETFs are exchange-traded products, they differ significantly in structure and risk profile․ Understanding these differences is paramount for investors․
Key Differences Between ETNs and ETFs
This table highlights the key distinctions between ETNs and ETFs:
| Feature | ETN | ETF |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Debt Instrument | Fund holding underlying assets |
| Credit Risk | Yes, issuer risk | No issuer risk (generally) |
| Tracking Error | Potentially lower, due to tracking the index’s return directly | Can have tracking error due to fund management |
| Tax Efficiency | Can be more tax-efficient, potentially avoiding dividend distributions | May generate taxable distributions |
Risks Associated with Investing in ETNs
Investing in ETNs comes with inherent risks that investors must carefully consider before investing․ Credit risk is the biggest concern․
Key Risks to Consider
Here are some of the potential pitfalls of investing in ETNs:
- Credit Risk: The issuer could default on its obligation, leading to a loss of investment․
- Liquidity Risk: Some ETNs may have low trading volumes, making it difficult to buy or sell shares․
- Tracking Error: Although ETNs aim to track an index, they may not perfectly replicate its performance․
- Call Risk: The issuer may redeem the ETN before maturity, potentially at an unfavorable price․
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About ETNs
This section answers common questions about ETNs to further clarify their nature and suitability for different investors․
- What is the benefit of investing in an ETN?
ETNs can provide access to niche market segments or investment strategies that may be difficult to access through other investment vehicles․ They can also offer potential tax advantages․ - How are ETNs taxed?
ETN taxation can be complex and depends on the specific structure of the ETN․ Consult with a tax advisor for personalized guidance․ - Are ETNs suitable for all investors?
ETNs are generally considered riskier than ETFs due to the credit risk of the issuer․ They are best suited for sophisticated investors who understand the risks involved․ - How do I research ETNs before investing?
Review the prospectus for the ETN, which provides detailed information about its structure, risks, and fees․ Also, research the issuer’s credit rating․ - Where can I find more information about ETNs?
Consult with a financial advisor or research reputable financial websites and resources․