The heart of modern transportation, the every car engine, is a marvel of engineering, a complex system of precisely timed events working in concert to convert fuel into motion. It’s more than just a source of power; it’s a carefully orchestrated ballet of pistons, valves, and combustion. Understanding the intricacies of how every car engine operates reveals a deeper appreciation for the technology that propels our daily lives. This article delves into the fascinating world of internal combustion, exploring its components, functions, and the future of automotive propulsion.
The Four-Stroke Cycle: The Engine’s Rhythm
The vast majority of car engines operate on the four-stroke cycle, a process repeated continuously to generate power. These strokes, intake, compression, combustion (power), and exhaust, each play a crucial role in the overall function of the engine. Let’s break down each stroke:
- Intake: The piston moves down, creating a vacuum that draws a mixture of air and fuel into the cylinder.
- Compression: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture, which increases its temperature and readiness for combustion.
- Combustion (Power): The spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing a rapid expansion that forces the piston down, generating power.
- Exhaust: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves up, pushing the burned gases out of the cylinder.
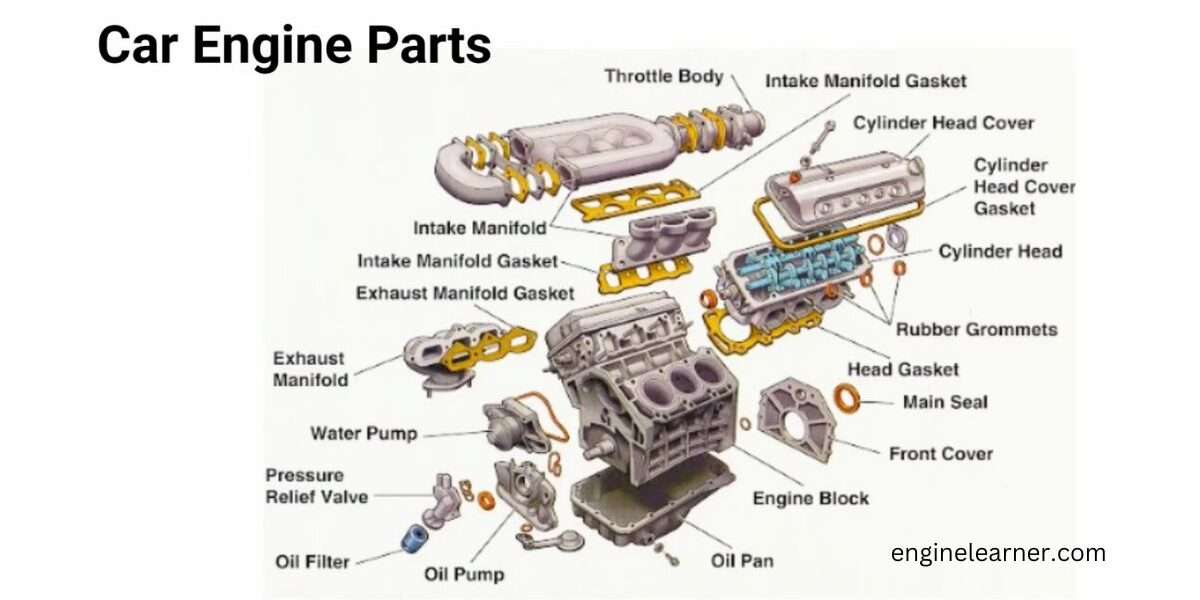
Key Components and Their Functions
Beyond the four-stroke cycle, several key components work together to ensure the engine’s smooth and efficient operation. These include:
The Cylinder Head: The Brain of the Operation
The cylinder head houses the valves, spark plugs, and combustion chambers. It controls the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the expulsion of exhaust gases. The design of the cylinder head significantly impacts engine performance and efficiency.
The Piston: The Engine’s Muscle
The piston is a cylindrical component that moves up and down within the cylinder. It’s connected to the crankshaft via a connecting rod, converting the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion. The piston’s rings create a tight seal against the cylinder walls, preventing combustion gases from escaping.
The Crankshaft: The Rotational Force
The crankshaft is a rotating shaft that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which is then transmitted to the wheels. Its design and construction are critical for handling the immense forces generated during combustion.
Alternative Engine Technologies
While the four-stroke internal combustion engine remains dominant, alternative engine technologies are emerging, driven by the need for greater efficiency and reduced emissions. These include hybrid engines, electric engines, and hydrogen fuel cell engines. These innovations represent the future of automotive propulsion.
The future of every car engine is undeniably evolving. The automotive industry is shifting its focus toward electrification and alternative fuel sources. While the familiar sound of the internal combustion engine may fade over time, its legacy as a pivotal technological achievement will remain forever etched in history.